Subarea 1: Stem Cell Aging
The individual research groups within Subarea 1 investigate the causes and consequences of stem cell aging. The research work spans from basic model organisms over genetic mouse models up to humanized mouse models engrafted with human stem cells.
According to the FLI, with the closure of two groups since 2016 the representation of invertebrate models of stem cell research was reduced in Subarea 1. The institute presumes that the recruitment of new groups should fill this gap.
The research is defined by four focus areas:
- Cell-intrinsic mechanisms limiting the function of aging stem and progenitor cells,
- Aging-associated alterations of stem cell niches and the systemic environment,
- Mechanisms of clonal selection and epigenetic drifts in stem cell aging, and
- Microbiota- and metabolism-induced impairments in stem cell function during aging (in context of the new focus area Microbiota and Aging currently being built up within Subarea 2).
Research focus of Subarea 1.
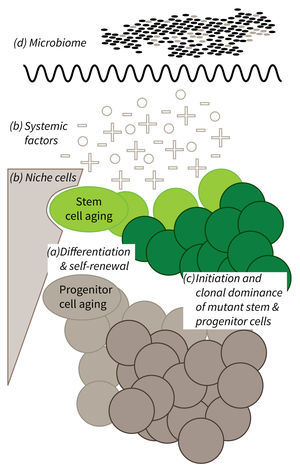
a) It is currently not well understood what mechanisms impair cellular functions in aging. b) The relative contribution of niche cells and systemic acting factors on stem cell aging have yet to be determined in different tissues. c) Clonal expansion of mutant cells associates with disease development in aging humans. Mechanistically, the process remains poorly understood. Changes in color intensity depict clonal dominance originating from stem (green) or progenitor cells (gray). d) Emerging evidences indicate that aging associated alter ations in microbiota influence stem cell function and vice versa.
Publications
(since 2016)
2020
- Elevated Hedgehog activity contributes to attenuated DNA damage responses in aged hematopoietic cells.
Scheffold A, Baig AH, Chen Z, von Löhneysen SE, Becker F, Morita Y, Avila AI, Groth M, Lechel A, Schmid F, Kraus JM, Kestler HA, Stilgenbauer S, Philipp M, Burkhalter MD
Leukemia 2020, 34(4), 1125-34 - Wnt7a Counteracts Cancer Cachexia.
Schmidt M, Poser C, von Maltzahn J
Mol Ther Oncolytics 2020, 16, 134-46 - Isolation and ex vivo cultivation of single myofibers from porcine muscle.
Stange K, Ahrens HE, von Maltzahn J, Röntgen M
In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 2020, 56(8), 585-92 - The role of Igf2bp2 in hematopoietic stem cell aging
Suo M
Dissertation 2020, Jena, Germany - Dietary restriction increases protective gut bacteria to rescue lethal methotrexate-induced intestinal toxicity.
Tang D, Zeng T, Wang Y, Cui H, Wu J, Zou B, Tao Z, Zhang L, Garside GB, Tao S
Gut Microbes 2020, 1(1714401), 1-21 - Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell-restricted Cdx2 expression induces transformation to myelodysplasia and acute leukemia.
Vu T, Straube J, Porter AH, Bywater M, Song A, Ling V, Cooper L, Pali G, Bruedigam C, Jacquelin S, Green J, Magor G, Perkins A, Chalk AM, Walkley CR, Heidel FH, Mukhopadhyay P, Cloonan N, Gröschel S, Mallm JP, Fröhling S, Scholl C, Lane SW
Nat Commun 2020, 11(1), 3021 - High Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Activity Sensitizes Murine Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells to DNA Damage.
Wang Y, Cui H, Tao S, Zeng T, Wu J, Tao Z, Zhang L, Zou B, Chen Z, Garside GB, Tang D
Stem Cell Rev Rep 2020, 16(1), 212-21 - S1P lyase inhibition protects against sepsis by promoting disease tolerance via the S1P/S1PR3 axis.
Weigel C, Hüttner SS, Ludwig K, Krieg N, Hofmann S, Schröder NH, Robbe L, Kluge S, Nierhaus A, Winkler MS, Rubio I, von Maltzahn J, Spiegel S, Gräler MH
EBioMedicine 2020, 58, 102898 - Ontogeny of arterial macrophages defines their functions in homeostasis and inflammation.
Weinberger T, Esfandyari D, Messerer D, Percin G, Schleifer C, Thaler R, Liu L, Stremmel C, Schneider V, Vagnozzi RJ, Schwanenkamp J, Fischer M, Busch K, Klapproth K, Ishikawa-Ankerhold H, Klösges L, Titova A, Molkentin JD, Kobayashi Y, Engelhardt S, Massberg S, Waskow C, Perdiguero EG, Schulz C
Nat Commun 2020, 11(1), 4549