Subarea 3: Genetics and Epigenetics of Aging
The focus of Subarea 3 is on genetic and epigenetic determinants of life- and health span as well as aging in fish, rodents and humans. This line of research builds on the expertise of the institute in comparative and functional genomics.
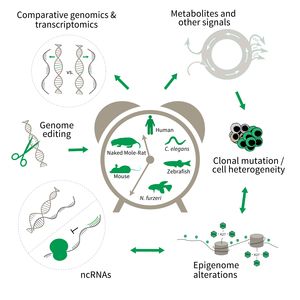
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Comparative genomics in short- and long-lived models of aging,
- Genomic engineering in N. furzeri,
- Epigenetics of aging,
- Non-coding RNAs in aging, and
- Comparative transcriptomics of aging.
Research focus of Subarea 3.
To uncover causative factors for aging, comparative genomics in short- and long-lived model systems are applied. Functional genomics is used to identify novel pathways contribute to aging of an organism and to validate the functional relevance of genetic and epigenetic changes that occur during aging. Furthermore, genetic risk factors for aging-related diseases are identified and functionally tested. The future development of the Subarea aims to integrate changes in host-microbiota interactions during aging, and how these influence clonal mutation and epigenetic alterations through metabolites and other signals.
Publications
(since 2016)
2018
- Regulation of RNA Polymerase I Transcription in Development, Disease, and Aging.
Sharifi S, Bierhoff H
Annu Rev Biochem 2018, 87, 51-73 - The Definition of Open Reading Frame Revisited.
Sieber P, Platzer M, Schuster S
Trends Genet 2018, 34(3), 167-70 - Generation and characterization of telomerase (tert) mutants in Nothobranchius furzeri.
Singer P
Dissertation 2018, Jena, Germany - The microRNA miR-21 Is a Mediator of FGF8 Action on Cortical COUP-TFI Translation.
Terrigno M, Bertacchi M, Pandolfini L, Baumgart M, Calvello M, Cellerino A, Studer M, Cremisi F
Stem Cell Reports 2018, 11(3), 756-69 - Corrigendum: Regulation of microRNA expression in the neuronal stem cell niches during aging of the short-lived annual fish Nothobranchius furzeri.
Terzibasi Tozzini E, Savino A, Ripa R, Battistoni G, Baumgart M, Cellerino A
Front Cell Neurosci 2018, 12, 227 Erratum for Front Cell Neurosci 2014 volume 8 page 51 - Rapidly evolving changes and gene loss associated with host switching in Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis.
Viana MVC, Sahm A, Góes Neto A, Figueiredo HCP, Wattam AR, Azevedo V
PLoS One 2018, 13(11), e0207304 - Limited scope for reproductive senescence in wild populations of a short-lived fish.
Vrtílek M, Žák J, Blažek R, Polačik M, Cellerino A, Reichard M
Naturwissenschaften 2018, 105(11-12), 68
2017
- Tissue-, sex- and age-specific DNA methylation of rat glucocorticoid receptor gene promoter and insulin like growth factor 2 imprinting control region.
Agba OB, Lausser L, Huse K, Bergmeier C, Jahn N, Groth M, Bens M, Sahm A, Gall M, Witte OW, Kestler HA, Schwab M, Platzer M
Physiol Genomics 2017, 49(11), 690-702 APSselect for distinction in scholarship in the Physiological Genomics - Mutations in NOTCH1 PEST domain orchestrate CCL19-driven homing of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by modulating the tumor suppressor gene DUSP22.
Arruga F, Gizdic B, Bologna C, Cignetto S, Buonincontri R, Serra S, Vaisitti T, Gizzi K, Vitale N, Garaffo G, Mereu E, Diop F, Neri F, Incarnato D, Coscia M, Allan J, Piva R, Oliviero S, Furman RR, Rossi D, Gaidano G, Deaglio S
Leukemia 2017, 31(9), 1882-93 published during change of institution - PD-L1 up-regulation in melanoma increases disease aggressiveness and is mediated through miR-17-5p.
Audrito V, Serra S, Stingi A, Orso F, Gaudino F, Bologna C, Neri F, Garaffo G, Nassini R, Baroni G, Rulli E, Massi D, Oliviero S, Piva R, Taverna D, Mandalà M, Deaglio S
Oncotarget 2017, 8(9), 15894-911 published during change of institution