Subarea 2: Regeneration and Homeostasis of Organs in Aging
The main goal of Subarea 2 is to identify cellular and molecular pathways used to ensure effective organ maintenance and repair, and to unravel the mechanisms of their deterioration during aging. While stem cells are important for organ homeostasis, this Subarea does not per se directly addresses stem cell aging but rather focusses on the following focus areas:
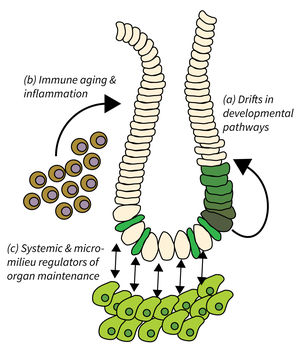
- Drifts in developmental pathways limiting organ maintenance in aging,
- Immune aging and inflammation, and
- Systemic and micro-milieu regulators of organ maintenance, regeneration, and disease development.
Research focus of Subarea 2
Organ maintenance is regulated by local and systemic factors, which are subject to aging-associated changes. Research of Subarea 2 focuses on the following research areas: a) Genetic and epigenetic modulation of developmental pathways has been shown to contribute to progressive aging and disease. It is critical to delineate mechanisms and consequences of aging-associated drifts to better understand organ maintenance during aging. b) Immunoaging and chronic inflammation elicits negative effects through reduced immune surveillance and aberrant organ repair and maintenance; all of which contributes to the evolution of organ pathologies and diseases during organismal aging. c) Furthermore, aging-associated alterations in systemic and extracellular factors derived from metabolic changes, microbiota alterations, chronic inflammation, senescent, or damaged cells might impinge on disease development and tumor initiation.
Publications
(since 2016)
2023
- Transcriptomes of aging brain, heart, muscle, and spleen from female and male African turquoise killifish.
Xu A, Teefy BB, Lu RJ, Nozownik S, Tyers AM, Valenzano DR, Benayoun BA
Sci Data 2023, 10(1), 695 published during change of institution
2022
- Inhibition of Cdk5 increases osteoblast differentiation and bone mass and improves fracture healing.
Ahmad M, Krüger BT, Kroll T, Vettorazzi S, Dorn AK, Mengele F, Lee S, Nandi S, Yilmaz D, Stolz M, Tangudu NK, Vázquez DC, Pachmayr J, Cirstea IC, Spasic MV, Ploubidou A, Ignatius A, Tuckermann J
Bone Res 2022, 10(1), 33 - Population size shapes the evolution of lifespan
Bagic M, Valenzano DR
bioRxiv 2022, https://www.doi.org/10.1101/2022 - The role of exosomes in inter-cellular and inter-organ communication of the peripheral nervous system.
Bischoff JP, Schulz A, Morrison H
FEBS Lett 2022, 596(5), 655-64 - Extensive age-dependent loss of antibody diversity in naturally short-lived turquoise killifish.
Bradshaw WJ, Poeschla M, Placzek A, Kean S, Valenzano DR
Elife 2022, 11, e65117 published during change of institution - Disruption of amphetamine sensitization by alteration of dendritic thin spines in the nucleus accumbens core.
Cai WT, Kim WY, Kwak MJ, Rim H, Lee SE, Riecken LB, Morrison H, Kim JH
J Neurochem 2022, 161(3), 266-80 - Planning preclinical confirmatory multicenter trials to strengthen translation from basic to clinical research –
a multi-stakeholder workshop report
Drude NI, Martinez-Gamboa L, Danziger M, Collazo A, Kniffert S, Wiebach J, Nilsonne G, Konietschke F, Piper SK, Pawel S, Micheloud C, Held L, Frommlet F, Segelcke D, Pogatzki-Zahn EM, Voelkl B, Friede T, Brunner E, Dempfle A, Haller B, Jung MJ, Riecken LB, Kuhn HG, Tenbusch M, Serna Higuita LM, Remarque EJ, Grüninger-Egli SL, Manske K, Kobold S, Rivalan M, Wedekind L, Wilcke JC, Boulesteix AL, Meinhardt MW, Spanagel R, Hettmer S, von Lüttichau I, Regina C, Dirnagl U, Toelch U
Translational Medicine Communications 2022, 7(24), doi 10.1186/s41231-022-00130-8 - A deep neural network provides an ultraprecise multi-tissue transcriptomic clock for the short-lived fish Nothobranchius furzeri and identifies predicitive genes translatable to human aging
Ferrari E, Reichwald K, Koch P, Groth M, Baumgart M, Cellerino A
bioRxiv 2022, doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.26.51761 - CD44 Contributes to the Regulation of MDR1 Protein and Doxorubicin Chemoresistance in Osteosarcoma.
Gerardo-Ramírez M, Keggenhoff FL, Giam V, Becker D, Groth M, Hartmann N, Straub BK, Morrison H, Galle PR, Marquardt JU, Herrlich P, Hartmann M
Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23(15), 8616 - Immediate predation risk alters the relationship between potential and realised selection on male traits in the Trinidad guppy Poecilia reticulata.
Glavaschi A, Cattelan S, Devigili A, Pilastro A
Proc Biol Sci 2022, 289(1982), 20220641