Subarea 2: Regeneration and Homeostasis of Organs in Aging
The main goal of Subarea 2 is to identify cellular and molecular pathways used to ensure effective organ maintenance and repair, and to unravel the mechanisms of their deterioration during aging. While stem cells are important for organ homeostasis, this Subarea does not per se directly addresses stem cell aging but rather focusses on the following focus areas:
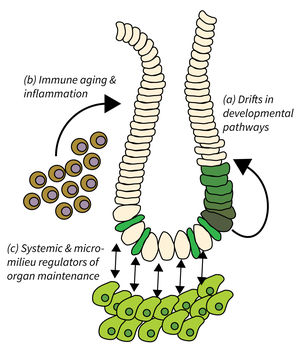
- Drifts in developmental pathways limiting organ maintenance in aging,
- Immune aging and inflammation, and
- Systemic and micro-milieu regulators of organ maintenance, regeneration, and disease development.
Research focus of Subarea 2
Organ maintenance is regulated by local and systemic factors, which are subject to aging-associated changes. Research of Subarea 2 focuses on the following research areas: a) Genetic and epigenetic modulation of developmental pathways has been shown to contribute to progressive aging and disease. It is critical to delineate mechanisms and consequences of aging-associated drifts to better understand organ maintenance during aging. b) Immunoaging and chronic inflammation elicits negative effects through reduced immune surveillance and aberrant organ repair and maintenance; all of which contributes to the evolution of organ pathologies and diseases during organismal aging. c) Furthermore, aging-associated alterations in systemic and extracellular factors derived from metabolic changes, microbiota alterations, chronic inflammation, senescent, or damaged cells might impinge on disease development and tumor initiation.
Publications
(since 2016)
2020
- C-Fiber Loss as a Possible Cause of Neuropathic Pain in Schwannomatosis.
Farschtschi SC, Mainka T, Glatzel M, Hannekum AL, Hauck M, Gelderblom M, Hagel C, Friedrich RE, Schuhmann MU, Schulz A, Morrison H, Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Luhmann J, Gerloff C, Bendszus M, Bäumer P, Mautner VF
Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21(10), 3569 - Inactivation of Horseradish Peroxidase by Acid for Sequential Chemiluminescent Western Blot.
Han S, Cui Y, Helbing DL
Biotechnol J 2020, 15(3), e1900397 - Neurofibromatosis type 2 and multiple sclerosis.
Helbing DL, Brodhun M, Tiedge O, Morrison H, Rosahl SK
MULT SCLER RELAT DIS 2020, 39, 101890 - Pathomechanisms in schwannoma development and progression.
Helbing DL, Schulz A, Morrison H
Oncogene 2020, 39(32), 5421-9 - Reduced proteasome activity in the aging brain results in ribosome stoichiometry loss and aggregation.
Kelmer Sacramento* E, Kirkpatrick* JM, Mazzetto* M, Baumgart M, Bartolome A, Di Sanzo S, Caterino C, Sanguanini M, Papaevgeniou N, Lefaki M, Childs D, Bagnoli S, Terzibasi Tozzini E, Di Fraia D, Romanov N, Sudmant PH, Huber W, Chondrogianni N, Vendruscolo M, Cellerino** A, Ori** A
Mol Syst Biol 2020, 16(6), e9596 * equal contribution, ** co-corresponding authors - A Caenorhabditis elegans ortholog of human selenium-binding protein 1 is a pro-aging factor protecting against selenite toxicity.
Köhnlein* K, Urban* N, Guerrero-Gómez D, Steinbrenner H, Urbánek P, Priebs J, Koch P, Kaether C, Miranda-Vizuete A, Klotz LO
Redox Biol 2020, 28, 101323 * equal contribution - CD44 (Cluster of differentiation 44) promotes osteosarcoma progression in mice lacking the tumor suppressor Merlin.
Ma* J, Klemm* J, Gerardo-Ramírez M, Frappart L, Castven D, Becker D, Zoch A, Parent R, Bartosch B, Minnich K, Giovannini M, Danckwardt S, Hartmann N, Morrison H, Herrlich** P, Marquardt** JU, Hartmann** M
Int J Cancer 2020, 147(9), 2564-77 * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors - The role of Hippo signaling in hematopoietic stem cell aging
Mura-Mészáros A
Dissertation 2020, Jena, Germany - SHP1 regulates a STAT6-ITGB3 axis in FLT3ITD-positive AML cells.
Reich D, Kresinsky A, Müller JP, Bauer R, Kallenbach J, Schnoeder TM, Heidel FH, Fässler R, Mann M, Böhmer FD, Jayavelu AK
Leukemia 2020, 34(5), 1444-9 - The stress-responsive gene GDPGP1/mcp-1 regulates neuronal glycogen metabolism and survival.
Schulz A, Sekine Y, Oyeyemi MJ, Abrams AJ, Basavaraju M, Han SM, Groth M, Morrison H, Strittmatter SM, Hammarlund M
J Cell Biol 2020, 219(2), doi: 10.1083/jcb.201807127