Subarea 5: Computational and Systems Biology of Aging
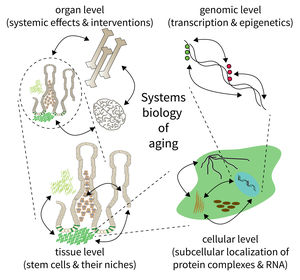
Subarea 5 focuses on the development of methods to analyse and understand complex biological systems. This work includes the design of computer algorithms and biostatistical approaches as well as the development of novel Omic strategies (i.e. genomics/epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) to study aging and aging-related diseases. According to the FLI, due to the Subarea's expertise in computational data analysis, it is deeply interconnected with all other Subareas. The Subarea hosts two critical core facilities (Life Science Computing, Proteomics) and provides consulting services in statistics. Furthermore, it organizes courses on data analysis and statistics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Mapping extrinsic and intrinsic factors influencing stem cells during aging,
- Integration of spatiotemporal proteomics and transcriptomics data,
- Comprehensive evaluation of qualitative and quantitative expression changes,
- Identification and analysis of epigenomic alterations during aging and age-related diseases, and
- Network analysis of genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic alterations during aging.
Research focus of Subarea 5.
The biology of aging can be viewed as a multilayered array of networks at the level of organs, cells, molecules, and genes. The FLI wants to meet this complexity by establishing the new Subarea on “Computational and Systems Biology of Aging”. The overall goal is to interconnect research at different scales, taking place in Subareas 1-4 of the Institute’s research program. The new group on Systems Biology will integrate data from networks at multiple scales and will thus point to mechanisms and interactions that would not be seen in unilayer approaches.
Publications
(since 2016)
2024
- Pipeline Olympics: continuable benchmarking of computational workflows for DNA methylation sequencing data against an experimental gold-standard
Lin YY, Breuer K, Weichenhan D, Lafrenz P, Wilk A, Chepeleva M, Mücke O, Schönung M, Petermann F, Kensche P, Weiser L, Thommen F, Giacomelli G, Nordstroem K, Gonzales-Avalos E, Merkel A, Kretzmer H, Fischer J, Krämer S, Iskar M, Wolf S, Buchhalter I, Esteller M, Lawerenz C, Twardziok S, Zapatka M, Hovestadt V, Schlesner M, Schulz M, Hoffmann S, Gerhauser C, Walter J, Hartmann M, B.Lipka D, Assenov Y, Bock C, Plass C, Toth R, Lutsik P
bioRxiv 2024, https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09. - Role of protein degradation and synthesis in proteostasis loss during the vertebrate brain aging
Marino A
Dissertation 2024, Jena, Germany - Polyamines sustain epithelial regeneration in aged intestines by modulating protein homeostasis
Minetti A, Omrani O, Brenner C, Allies G, Imada S, Rösler J, Khawaled S, Cansiz F, W.Meckelmann S, Gebert N, Heinze I, Lu J, Spengler K, Rasa M, Heller R, Yilmaz O, Tasdogan A, Neri F, Ori A
bioRxiv 2024, https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07. - Glycerophosphodiesters inhibit lysosomal phospholipid catabolism in Batten disease.
Nyame K, Hims A, Aburous A, Laqtom NN, Dong W, Medoh UN, Heiby JC, Xiong J, Ori A, Abu-Remaileh M
Mol Cell 2024, 84(7), 1354-1364.e9 - Nonlinear DNA methylation trajectories in aging male mice.
Olecka* M, van Bömmel* A, Best L, Haase M, Foerste S, Riege K, Dost T, Flor S, Witte OW, Franzenburg S, Groth M, von Eyss B, Kaleta C, Frahm C, Hoffmann S
Nat Commun 2024, 15(1), 3074 * equal contribution - iSODA: A Comprehensive Tool for Integrative Omics Data Analysis in Single- and Multi-Omics Experiments
Olivier-Jimenez D, J.E.Derks R, Harari O, Cruchaga C, Ali M, Ori A, Di Fraia D, Cabukusta B, Henrie A, Giera M, Mohammed Y
bioRxiv 2024, https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.08. - Aging-associated decline of phosphatidylcholine synthesis is a malleable trigger of natural mitochondrial aging
Poliezhaieva T, Alonso Pernas P, Espada L, Bayar M, Li Y, Melike Dönertaş H, A.Ermolaeva M
bioRxiv 2024, https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.04. - The Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus) genome provides insights into extreme longevity
Sahm A, Cherkasov* A, Liu* H, Voronov D, Siniuk K, Schwarz R, Ohlenschlaeger O, Foerste S, Bens M, Groth M, Goerlich I, Paturej S, Klages S, Braendl B, Olsen J, Bushnell P, Bech Poulsen A, Ferrando S, Garibaldi F, Lorenzo Drago D, Terzibasi Tozzini E, Mueller FJ, Fischer M, Kretzmer H, Domenici** P, Fleng Steffensen** J, Cellerino** A, Hoffmann** S
bioRxiv 2024, 10.1101/2024.09.09.611499 * equal contribution, ** co-corresponding authors - Hydra has mammal-like mutation rates facilitating fast adaptation despite its nonaging phenotype.
Sahm A, Riege K, Groth M, Bens M, Kraus J, Fischer M, Kestler H, Englert C, Schaible R, Platzer M, Hoffmann S
Genome Res 2024, 34(12), 2217-28 - Remodelling of the cardiac extracellular matrix proteome during chronological and pathological ageing.
Santinha D, Vilaça A, Estronca L, Schüler SC, Bartoli C, De Sandre-Giovannoli A, Figueiredo A, Quaas M, Pompe T, Ori** A, Ferreira** L
Mol Cell Proteomics 2024, 23(1), 100706 ** co-corresponding authors