Subarea 5: Computational and Systems Biology of Aging
Subarea 5 focuses on the development of methods to analyse and understand complex biological systems. This work includes the design of computer algorithms and biostatistical approaches as well as the development of novel Omic strategies (i.e. genomics/epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) to study aging and aging-related diseases. According to the FLI, due to the Subarea's expertise in computational data analysis, it is deeply interconnected with all other Subareas. The Subarea hosts two critical core facilities (Life Science Computing, Proteomics) and provides consulting services in statistics. Furthermore, it organizes courses on data analysis and statistics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Mapping extrinsic and intrinsic factors influencing stem cells during aging,
- Integration of spatiotemporal proteomics and transcriptomics data,
- Comprehensive evaluation of qualitative and quantitative expression changes,
- Identification and analysis of epigenomic alterations during aging and age-related diseases, and
- Network analysis of genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic alterations during aging.
Research focus of Subarea 5.
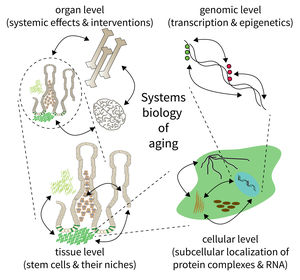
The biology of aging can be viewed as a multilayered array of networks at the level of organs, cells, molecules, and genes. The FLI wants to meet this complexity by establishing the new Subarea on “Computational and Systems Biology of Aging”. The overall goal is to interconnect research at different scales, taking place in Subareas 1-4 of the Institute’s research program. The new group on Systems Biology will integrate data from networks at multiple scales and will thus point to mechanisms and interactions that would not be seen in unilayer approaches.
Publications
(since 2016)
2025
- Machine Learning and Omic Data for Prediction of Health and Chronic Diseases
Olenik M, Dönertaş HM
In: Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (edited by Shoba R, Mario C, Asif MK) 2025, 6, 365-388, Elsevier, Amsterdam - iSODA: A Comprehensive Tool for Integrative Omics Data Analysis in Single- and Multi-Omics Experiments.
Olivier-Jimenez D, Derks RJE, Harari O, Cruchaga C, Ali M, Ori A, Di Fraia D, Cabukusta B, Henrie A, Giera M, Mohammed Y
Anal Chem 2025 (epub ahead of print) - Protecting cell cycle integrity: enhanced start-codon stringency in mitosis.
Omrani O, Siniuk K, Fischer M
Signal Transduct Target Ther 2025, 10(1), 34 - Embryonic macrophages orchestrate niche cell homeostasis for the establishment of the definitive hematopoietic stem cell pool.
Perçin** G, Riege K, Fröbel J, Metz J, Culemann S, Lesche M, Reinhardt S, Höfer T, Hoffmann S, Waskow** C
Nat Commun 2025, 16(1), 4428 ** co-corresponding authors - Replication stress responses in human lymphocytes change sex-specifically during aging.
Rall-Scharpf M, Schlotter D, Koch P, Szafranski K, Groth M, Sahm A, Biber S, Castaño BA, Heitmeir B, Zengerling F, Deniz M, Dallmeier D, Braig S, Bonig H, Milyavsky M, Pospiech H, Wiesmüller L
Nucleic Acids Res 2025, 53(11) - The master male sex determinant Gdf6Y of the turquoise killifish arose through allelic neofunctionalization.
Richter A, Mörl H, Thielemann M, Kleemann M, Geißen R, Schwarz R, Albertz C, Koch P, Petzold A, Kroll T, Groth M, Hartmann N, Herpin A, Englert C
Nat Commun 2025, 16(1), 540 - UV laser crosslinking uncovers novel DNA-binding pattern of CTCF*
Stanko C, Gupse Özcan S, Stengel S, Szymański Ł, Steube A, Fischer M, Brioli A, Schenk T
bioRxiv 2025, https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.05. - Age-dependent gut microbiota dynamics and their association with male fitness traits in Drosophila melanogaster
Sultanova** * Z, Dönertaş** * HM, Hita A, Aguilar P, Dag B, Ignacio Lucas-Lledo J, Latorre A, Carazo P
bioRxiv 2025, https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.05. * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors - Dynamics of HBV biomarkers during nucleos(t)ide analog treatment: A 14-year study.
van Bömmel F, Degasperi E, van Bömmel A, Facchetti F, Sambarino D, Deichsel D, Brehm J, Kamga Wouambo R, Maier M, Pfefferkorn M, Berg T, Lampertico P
Hepatol Commun 2025, 9(6) - Author Correction: Large-scale benchmarking of circRNA detection tools reveals large differences in sensitivity but not in precision.
Vromman M, Anckaert J, Bortoluzzi S, Buratin A, Chen CY, Chu Q, Chuang TJ, Dehghannasiri R, Dieterich C, Dong X, Flicek P, Gaffo E, Gu W, He C, Hoffmann S, Izuogu O, Jackson MS, Jakobi T, Lai EC, Nuytens J, Salzman J, Santibanez-Koref M, Stadler P, Thas O, Vanden Eynde E, Verniers K, Wen G, Westholm J, Yang L, Ye CY, Yigit N, Yuan GH, Zhang J, Zhao F, Vandesompele J, Volders PJ
Nat Methods 2025 (epub ahead of print)