Subarea 5: Computational and Systems Biology of Aging
Subarea 5 focuses on the development of methods to analyse and understand complex biological systems. This work includes the design of computer algorithms and biostatistical approaches as well as the development of novel Omic strategies (i.e. genomics/epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) to study aging and aging-related diseases. According to the FLI, due to the Subarea's expertise in computational data analysis, it is deeply interconnected with all other Subareas. The Subarea hosts two critical core facilities (Life Science Computing, Proteomics) and provides consulting services in statistics. Furthermore, it organizes courses on data analysis and statistics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Mapping extrinsic and intrinsic factors influencing stem cells during aging,
- Integration of spatiotemporal proteomics and transcriptomics data,
- Comprehensive evaluation of qualitative and quantitative expression changes,
- Identification and analysis of epigenomic alterations during aging and age-related diseases, and
- Network analysis of genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic alterations during aging.
Research focus of Subarea 5.
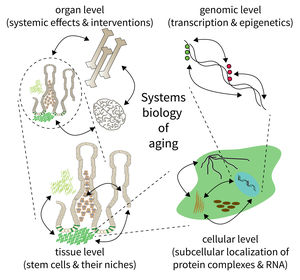
The biology of aging can be viewed as a multilayered array of networks at the level of organs, cells, molecules, and genes. The FLI wants to meet this complexity by establishing the new Subarea on “Computational and Systems Biology of Aging”. The overall goal is to interconnect research at different scales, taking place in Subareas 1-4 of the Institute’s research program. The new group on Systems Biology will integrate data from networks at multiple scales and will thus point to mechanisms and interactions that would not be seen in unilayer approaches.
Publications
(since 2016)
2023
- A protocol for the use of cloud-based quantum computers for logical network analysis of biological systems.
Weidner FM, Rossini M, Ankerhold J, Kestler HA
STAR Protoc 2023, 4(3), 102438 - Leveraging quantum computing for dynamic analyses of logical networks in systems biology.
Weidner FM, Schwab JD, Wölk S, Rupprecht F, Ikonomi N, Werle SD, Hoffmann S, Kühl M, Kestler HA
PATTERNS 2023, 4(3), 100705 - Author Correction: Butler enables rapid cloud-based analysis of thousands of human genomes.
Yakneen S, Waszak SM, PCAWG Technical Working Group, Gertz M, Korbel JO, PCAWG Consortium
Nat Biotechnol 2023, 41(4), 577 - Author Correction: Comprehensive molecular characterization of mitochondrial genomes in human cancers.
Yuan Y, Ju YS, Kim Y, Li J, Wang Y, Yoon CJ, Yang Y, Martincorena I, Creighton CJ, Weinstein JN, Xu Y, Han L, Kim HL, Nakagawa H, Park K, Campbell PJ, Liang H, PCAWG Consortium
Nat Genet 2023, 55(6), 1078 - Author Correction: The landscape of viral associations in human cancers.
Zapatka M, Borozan I, Brewer DS, Iskar M, Grundhoff A, Alawi M, Desai N, Sültmann H, Moch H, PCAWG Pathogens, Cooper CS, Eils R, Ferretti V, Lichter P, PCAWG Consortium
Nat Genet 2023, 55(6), 1077
2022
- Investigating the proteasome interaction network using proximity ligation coupled to mass spectrometry
Bartolome A
Dissertation 2022, Jena, Germany - Novel biochemical, structural, and systems insights into inflammatory signaling revealed by contextual interaction proteomics.
Ciuffa R, Uliana F, Mannion J, Mehnert M, Tenev T, Marulli C, Satanowski A, Keller LML, Rodilla Ramírez PN, Ori A, Gstaiger M, Meier P, Aebersold R
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119(40), e2117175119 - p53-mediated AKT and mTOR inhibition requires RFX7 and DDIT4 and depends on nutrient abundance.
Coronel* L, Häckes* D, Schwab* K, Riege K, Hoffmann** S, Fischer** M
Oncogene 2022, 41(7), 1063-9 * equal contribution, ** co-corresponding authors - Conserved exchange of paralog proteins during neuronal differentiation.
Di Fraia D, Anitei M, Mackmull MT, Parca L, Behrendt L, Andres-Pons A, Gilmour D, Helmer Citterich M, Kaether C, Beck M, Ori A
Life Sci Alliance 2022, 5(6), e202201397 - Metabolic determination of cell fate through selective inheritance of mitochondria.
Döhla J, Kuuluvainen E, Gebert N, Amaral A, Englund JI, Gopalakrishnan S, Konovalova S, Nieminen AI, Salminen ES, Torregrosa Muñumer R, Ahlqvist K, Yang Y, Bui H, Otonkoski T, Käkelä R, Hietakangas V, Tyynismaa H, Ori A, Katajisto P
Nat Cell Biol 2022, 24(2), 148-54