Subarea 5: Computational and Systems Biology of Aging
Subarea 5 focuses on the development of methods to analyse and understand complex biological systems. This work includes the design of computer algorithms and biostatistical approaches as well as the development of novel Omic strategies (i.e. genomics/epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) to study aging and aging-related diseases. According to the FLI, due to the Subarea's expertise in computational data analysis, it is deeply interconnected with all other Subareas. The Subarea hosts two critical core facilities (Life Science Computing, Proteomics) and provides consulting services in statistics. Furthermore, it organizes courses on data analysis and statistics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Mapping extrinsic and intrinsic factors influencing stem cells during aging,
- Integration of spatiotemporal proteomics and transcriptomics data,
- Comprehensive evaluation of qualitative and quantitative expression changes,
- Identification and analysis of epigenomic alterations during aging and age-related diseases, and
- Network analysis of genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic alterations during aging.
Research focus of Subarea 5.
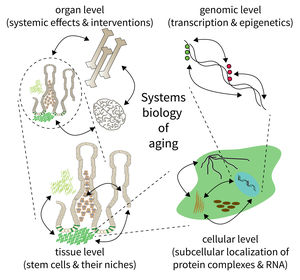
The biology of aging can be viewed as a multilayered array of networks at the level of organs, cells, molecules, and genes. The FLI wants to meet this complexity by establishing the new Subarea on “Computational and Systems Biology of Aging”. The overall goal is to interconnect research at different scales, taking place in Subareas 1-4 of the Institute’s research program. The new group on Systems Biology will integrate data from networks at multiple scales and will thus point to mechanisms and interactions that would not be seen in unilayer approaches.
Publications
(since 2016)
2021
- Favorable outcome of NUTM1-rearranged infant and pediatric B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a collaborative international study.
Boer JM, Valsecchi MG, Hormann FM, Antić Ž, Zaliova M, Schwab C, Cazzaniga G, Arfeuille C, Cavé H, Attarbaschi A, Strehl S, Escherich G, Imamura T, Ohki K, Grüber TA, Sutton R, Pastorczak A, Lammens T, Lambert F, Li CK, Carrillo de Santa Pau E, Hoffmann S, Möricke A, Harrison CJ, Den Boer ML, De Lorenzo P, Stam RW, Bergmann AK, Pieters R
Leukemia 2021, 35(10), 2978-82 - Surprisingly long survival of premature conclusions about naked mole-rat biology.
Braude S, Holtze S, Begall S, Brenmoehl J, Burda H, Dammann P, Del Marmol D, Gorshkova E, Henning Y, Hoeflich A, Höhn A, Jung T, Hamo D, Sahm A, Shebzukhov Y, Šumbera R, Miwa S, Vyssokikh MY, von Zglinicki T, Averina O, Hildebrandt TB
Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 2021, 96(2), 376-93 - Epigenetic Modifications Associated with Maternal Anxiety during Pregnancy and Children's Behavioral Measures.
Cao-Lei L, van den Heuvel MI, Huse K, Platzer M, Elgbeili G, Braeken MAKA, Otte RA, Witte OW, Schwab M, Van den Bergh BRH
Cells 2021, 10(9), 2421 - Transcription factor RFX7 governs a tumor suppressor network in response to p53 and stress.
Coronel L, Riege K, Schwab K, Förste S, Häckes D, Semerau L, Bernhart SH, Siebert R, Hoffmann** S, Fischer** M
Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49(13), 7437-56 ** co-corresponding authors - Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Carrying 5-Fluorouracil in Combination with Magnetic Hyperthermia Induce Thrombogenic Collagen Fibers, Cellular Stress, and Immune Responses in Heterotopic Human Colon Cancer in Mice.
Dabaghi M, Rasa SMM, Cirri E, Ori A, Neri F, Quaas R, Hilger I
Pharmaceutics 2021, 13(10), 1625 - Tnfaip2/exoc3-driven lipid metabolism is essential for stem cell differentiation and organ homeostasis.
Deb S, Felix DA, Koch P, Deb MK, Szafranski K, Buder K, Sannai M, Groth M, Kirkpatrick J, Pietsch S, Gollowitzer A, Groß A, Riemenschneider P, Koeberle A, González-Estévez** C, Rudolph** KL
EMBO Rep 2021, 22(1), e49328 ** co-corresponding authors - Abundance and size of hyaluronan in naked mole-rat tissues and plasma.
Del Marmol D, Holtze S, Kichler N, Sahm A, Bihin B, Bourguignon V, Dogné S, Szafranski K, Hildebrandt TB, Flamion B
Sci Rep 2021, 11(1), 7951 - Mapping sites of carboxymethyllysine modification on proteins reveals its consequences for proteostasis and cell proliferation
Di Sanzo S
Dissertation 2021, Jena, Germany - Mapping protein carboxymethylation sites provides insights into their role in proteostasis and cell proliferation.
Di Sanzo* S, Spengler* K, Leheis A, Kirkpatrick JM, Rändler TL, Baldensperger T, Dau T, Henning C, Parca L, Marx C, Wang ZQ, Glomb MA, Ori** A, Heller** R
Nat Commun 2021, 12(1), 6743 * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors - Mice Are Not Humans: The Case of p53.
Fischer M
Trends Cancer 2021, 7(1), 12-4