Subarea 3: Genetics and Epigenetics of Aging
The focus of Subarea 3 is on genetic and epigenetic determinants of life- and health span as well as aging in fish, rodents and humans. This line of research builds on the expertise of the institute in comparative and functional genomics.
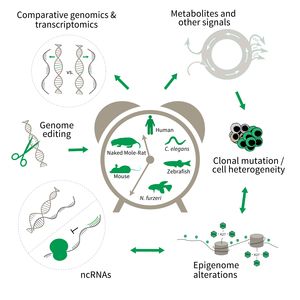
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Comparative genomics in short- and long-lived models of aging,
- Genomic engineering in N. furzeri,
- Epigenetics of aging,
- Non-coding RNAs in aging, and
- Comparative transcriptomics of aging.
Research focus of Subarea 3.
To uncover causative factors for aging, comparative genomics in short- and long-lived model systems are applied. Functional genomics is used to identify novel pathways contribute to aging of an organism and to validate the functional relevance of genetic and epigenetic changes that occur during aging. Furthermore, genetic risk factors for aging-related diseases are identified and functionally tested. The future development of the Subarea aims to integrate changes in host-microbiota interactions during aging, and how these influ ence clonal mutation and epigenetic alterations through metabolites and other signals.
Publications
(since 2016)
2023
- Identification of altered miRNAs and their targets in placenta accreta.
Murrieta-Coxca JM, Barth E, Fuentes-Zacarias P, Gutiérrez-Samudio RN, Groten T, Gellhaus A, Köninger A, Marz M, Markert UR, Morales-Prieto DM
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1021640 - Author Correction: IFNγ-Stat1 axis drives aging-associated loss of intestinal tissue homeostasis and regeneration.
Omrani* O, Krepelova* A, Rasa SMM, Sirvinskas D, Lu J, Annunziata F, Garside G, Bajwa S, Reinhardt S, Adam L, Käppel S, Ducano N, Donna D, Ori A, Oliviero S, Rudolph KL, Neri F
Nat Commun 2023, 14(1), 6302 * equal contribution - IFNγ-Stat1 axis drives aging-associated loss of intestinal tissue homeostasis and regeneration.
Omrani* O, Krepelova* A, Rasa SMM, Sirvinskas D, Lu J, Annunziata F, Garside G, Bajwa S, Reinhardt S, Adam L, Käppel S, Ducano N, Donna D, Ori A, Oliviero S, Rudolph KL, Neri F
Nat Commun 2023, 14(1), 6109 * equal contribution - The Tgf-β family member Gdf6Y determines the male sex in Nothobranchius furzeri by suppressing oogenesis-inducing genes
Richter A, Mörl H, Thielemann M, Kleemann M, Geißen R, Schwarz R, Albertz C, Koch P, Petzold A, Groth M, Hartmann N, Herpin A, Englert C
bioRxiv 2023, 10.1101/2023.05.26.542338 - Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Review of Current Virus Databases.
Ritsch M, Cassman NA, Saghaei S, Marz M
Viruses 2023, 15(9) - Explaining variation in individual aging, its sources, and consequences: A comprehensive conceptual model of human aging.
Rothermund K, Englert C, Gerstorf D
Gerontology 2023, 69(12), 1437-47 - The African killifish: A short-lived vertebrate model to study the biology of sarcopenia and longevity.
Ruparelia AA, Salavaty A, Barlow CK, Lu Y, Sonntag C, Hersey L, Eramo MJ, Krug J, Reuter H, Schittenhelm RB, Ramialison M, Cox A, Ryan MT, Creek DJ, Englert C, Currie PD
Aging Cell 2023, 23(1), e13862 - Detection of reproducible liver cancer specific ligand-receptor signaling in blood
Safrastyan A, Wollny D
bioRxiv 2023, 10.1101/2023.09.25.559274 - Decoding cell-type contributions to the cfRNA transcriptomic landscape of liver cancer.
Safrastyan** A, Zu Siederdissen CH, Wollny** D
Hum Genomics 2023, 17(1), 90 ** co-corresponding authors - Antioxidants Prevent the Effects of Physical Exercise on Visual Cortical Plasticity.
Sansevero G, Consorti A, Di Marco I, Terzibasi Tozzini E, Cellerino** A, Sale** A
Cells 2023, 12(1), doi.org/10.3390/cells12010048 ** co-senior authors