Subarea 1: Stem Cell Aging
The individual research groups within Subarea 1 investigate the causes and consequences of stem cell aging. The research work spans from basic model organisms over genetic mouse models up to humanized mouse models engrafted with human stem cells.
According to the FLI, with the closure of two groups since 2016 the representation of invertebrate models of stem cell research was reduced in Subarea 1. The institute presumes that the recruitment of new groups should fill this gap.
The research is defined by four focus areas:
- Cell-intrinsic mechanisms limiting the function of aging stem and progenitor cells,
- Aging-associated alterations of stem cell niches and the systemic environment,
- Mechanisms of clonal selection and epigenetic drifts in stem cell aging, and
- Microbiota- and metabolism-induced impairments in stem cell function during aging (in context of the new focus area Microbiota and Aging currently being built up within Subarea 2).
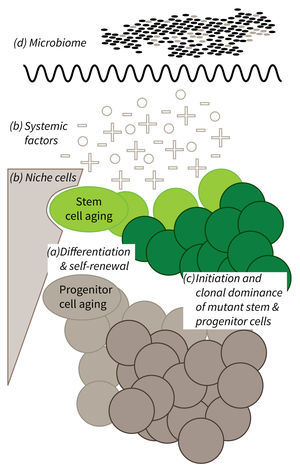
Research focus of Subarea 1.
a) It is currently not well understood what mechanisms impair cellular functions in aging. b) The relative contribution of niche cells and systemic acting factors on stem cell aging have yet to be determined in different tissues. c) Clonal expansion of mutant cells associates with disease development in aging humans. Mechanistically, the process remains poorly understood. Changes in color intensity depict clonal dominance originating from stem (green) or progenitor cells (gray). d) Emerging evidences indicate that aging associated alter ations in microbiota influence stem cell function and vice versa.
Publications
(since 2016)
2018
- Telomeric epigenetic response mediated by Gadd45a regulates stem cell aging and lifespan.
Diao D, Wang H, Li T, Shi Z, Jin X, Sperka T, Zhu X, Zhang M, Yang F, Cong Y, Shen L, Zhan Q, Yan J, Song Z, Ju Z
EMBO Rep 2018, 19(10), e45494 - JAK2-V617F promotes venous thrombosis through β1/β2 integrin activation.
Edelmann B, Gupta N, Schnoeder TM, Oelschlegel AM, Shahzad K, Goldschmidt J, Philipsen L, Weinert S, Ghosh A, Saalfeld FC, Nimmagadda SC, Müller P, Braun-Dullaeus R, Mohr J, Wolleschak D, Kliche S, Amthauer H, Heidel FH, Schraven B, Isermann B, Müller AJ, Fischer T
J Clin Invest 2018, 128(10), 4359-71 - Cellular and epigenetic drivers of stem cell ageing.
Ermolaeva** M, Neri** F, Ori** A, Rudolph** KL
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2018, 19(9), 594-610 ** co-corresponding authors - Epigenetic aging of human hematopoietic cells is not accelerated upon transplantation into mice.
Frobel J, Rahmig S, Franzen J, Waskow C, Wagner W
Clin Epigenetics 2018, 10, 67 published during change of institution - Telomeres in cancer.
Gunes C, Avila AI, Rudolph KL
Differentiation 2018, 99, 41-50 - Proteostasis is essential for planarian stem cell regulation and regeneration during starvation.
Gutierrez-Gutierrez O
Dissertation 2018, Jena, Germany - Influence of Scribble polarity complex on hematopoiesis and leukemia - a matter of where, when and how.
Heidel FH, Ellis S
Oncotarget 2018, 9(78), 34642-3 - RelB regulates Th17 differentiation in a cell-intrinsic manner.
Koliesnik IO, Andreas N, Romanov VS, Sreekantapuram S, Krljanac B, Haenold R, Weih F
Immunobiology 2018, 223(2), 191-9 - Epigenetic Erosion in Adult Stem Cells: Drivers and Passengers of Aging.
Kosan C, Heidel FH, Godmann M, Bierhoff H
Cells 2018, 7(12) - Mutational impact of culturing human pluripotent and adult stem cells.
Kuijk E, Jager M, van der Roest B, Locati M, Van Hoeck A, Korzelius J, Janssen R, Besselink N, Boymans S, van Boxtel R, Cuppen E
bioRxiv 2018, http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/430165