Subarea 1: Stem Cell Aging
The individual research groups within Subarea 1 investigate the causes and consequences of stem cell aging. The research work spans from basic model organisms over genetic mouse models up to humanized mouse models engrafted with human stem cells.
According to the FLI, with the closure of two groups since 2016 the representation of invertebrate models of stem cell research was reduced in Subarea 1. The institute presumes that the recruitment of new groups should fill this gap.
The research is defined by four focus areas:
- Cell-intrinsic mechanisms limiting the function of aging stem and progenitor cells,
- Aging-associated alterations of stem cell niches and the systemic environment,
- Mechanisms of clonal selection and epigenetic drifts in stem cell aging, and
- Microbiota- and metabolism-induced impairments in stem cell function during aging (in context of the new focus area Microbiota and Aging currently being built up within Subarea 2).
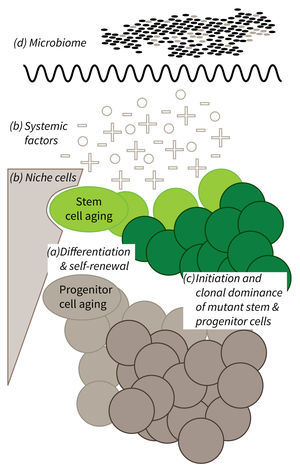
Research focus of Subarea 1.
a) It is currently not well understood what mechanisms impair cellular functions in aging. b) The relative contribution of niche cells and systemic acting factors on stem cell aging have yet to be determined in different tissues. c) Clonal expansion of mutant cells associates with disease development in aging humans. Mechanistically, the process remains poorly understood. Changes in color intensity depict clonal dominance originating from stem (green) or progenitor cells (gray). d) Emerging evidences indicate that aging associated alter ations in microbiota influence stem cell function and vice versa.
Publications
(since 2016)
2019
- Prospective isolation of non-hematopoietic cells of the niche and their differential molecular interactions with HSCs.
Mende* N, Jolly* A, Percin* GI, Günther M, Rostovskaya M, Krishnan SM, Oostendorp RAJ, Dahl A, Anastassiadis K, Höfer** T, Waskow** C
Blood 2019, 134(15), 1214-26 * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors - Differences in expression rather than methylation at placenta-specific imprinted loci is associated with intrauterine growth restriction.
Monteagudo-Sánchez A, Sánchez-Delgado M, Mora JRH, Santamaría NT, Gratacós E, Esteller M, de Heredia ML, Nunes V, Choux C, Fauque P, de Nanclares GP, Anton L, Elovitz MA, Iglesias-Platas I, Monk D
Clin Epigenetics 2019, 11(1), 35 - ORP3 is a tumor suppressor protein in the B-cell lineage of aging mice
Njeru SN
Dissertation 2019, Jena, Germany - Plasma VCAM1 levels correlate with disease severity in Parkinson's disease.
Perner C, Perner F, Gaur N, Zimmermann S, Witte OW, Heidel FH, Grosskreutz J, Prell T
J Neuroinflammation 2019, 16(1), 94 - Roles of JAK2 in Aging, Inflammation, Hematopoiesis and Malignant Transformation.
Perner F, Perner C, Ernst T, Heidel FH
Cells 2019, 8(8) - Loss of a proteostatic checkpoint in intestinal stem cells contributes to age-related epithelial dysfunction.
Rodriguez-Fernandez IA, Qi Y, Jasper H
Nat Commun 2019, 10(1), 1050 - Adult stem cells at work: regenerating skeletal muscle.
Schmidt M, Schüler SC, Hüttner SS, von Eyss B, von Maltzahn J
Cell Mol Life Sci 2019, 76(13), 2559-70 - Author Correction: Epigenetic stress responses induce muscle stem-cell ageing by Hoxa9 developmental signals.
Schwörer S, Becker F, Feller C, Baig AH, Köber U, Henze H, Kraus JM, Xin B, Lechel A, Lipka DB, Varghese CS, Schmidt M, Rohs R, Aebersold R, Medina KL, Kestler HA, Neri F, von Maltzahn** J, Tümpel** S, Rudolph** KL
Nature 2019, 572(7769), E11-5 ** co-corresponding authors - SIRT6 Is Responsible for More Efficient DNA Double-Strand Break Repair in Long-Lived Species.
Tian X, Firsanov D, Zhang Z, Cheng Y, Luo L, Tombline G, Tan R, Simon M, Henderson S, Steffan J, Goldfarb A, Tam J, Zheng K, Cornwell A, Johnson A, Yang JN, Mao Z, Manta B, Dang W, Zhang Z, Vijg J, Wolfe A, Moody K, Kennedy BK, Bohmann D, Gladyshev VN, Seluanov A, Gorbunova V
Cell 2019, 177(3), 622-638.e22 - AWD regulates timed activation of BMP signaling in intestinal stem cells to maintain tissue homeostasis.
Tracy Cai X, Li H, Safyan A, Gawlik J, Pyrowolakis G, Jasper H
Nat Commun 2019, 10(1), 2988